The excavation of the monument, known as Borobudur, has been ordered by Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles, the new British Governor of Java. Unlike the Dutch traders before him, Raffles is intrigued by the exotic stories and architecture of the Indonesian islands: "The antiquities of Java have not, till lately, excited much notice; nor have they yet been sufficiently explored. The pursuits of commerce have been too exclusive to allow there being much interest in the subject."
When Raffles comes to inspect the progress of his expedition, he finds a colossal pyramid, rising to a huge bell-shaped pinnacle. Lacking adequate historical records, Raffles is unable to determine the exact date of Borobudur's construction, but he does have some insight into the purpose of the structure: "The resemblance of the images which surround this monument to the figure of Buddha, has introduced an opinion that Borobudur was exclusively confined to the worship of that deity."
But there is no central altar or sanctuary in this temple. Instead, the galleries that ring the structure are covered with nearly three thousand bas-relief panels carved into the stone.
As word of the discovery spreads, scholars of Asian religions visit. They recognize Borobudur as the largest Buddhist temple in the world... and the most unusual. The panels depict the teachings of the Buddha, each familiar story a step in the pilgrim's progress. The galleries are designed to guide the faithful on a spiritual journey as they move upward from terrace to terrace, each level representing a higher plane of consciousness. In ancient times, pilgrims may have come from all over Southeast Asia to study the sacred texts full of mystery, meaning, meditation and morals. Borobudur is a three-dimensional guide to Enlightenment. But despite Raffles' best intentions, uncovering Borobudur has placed it in grave danger, as reports of the exotic temple attract a new breed of pilgrim. The local villagers are no longer superstitious of the monument, and now view it as a constant source of building materials.
Souvenir hunters decapitate many of the Buddhas and ship them to mansions and museums throughout the world. For the weary tourist, a teahouse is built high on the crumbling central stupa. According to Asian art historian, Jan Fontein, "Many of the Europeans who came to Asia, and many of the Asians themselves, because they had been converted to Islam, regarded these monuments as the work of heathen, and this prevented them from appreciating their true beauty."
But in 1885, an acc idental discovery rekindles interest in preserving this ancient treasure. J. W. Ijzerman, a Dutch architect involved in a restoration project, walks along the high processional path that surrounds the base of Borobudur. "And he noticed that the moldings of the wall continued underneath a crack that he saw in the floor," says Fontein. "This meant that all these stones must have been added at a time when part of the building was already finished."Ijzerman excitedly calls for a section of the path to be removed. When sixteen layers of stone have been pulled away, Ijzerman discovers another tier of panels quite unlike those of the upper galleries. These are portrayals of hellish tortures mixed with scenes of sweet pleasure. In all, one hundred sixty panels are uncovered. A few scenes had been left unfinished, with instructions to the stone carver inscribed in Sanskrit, and the style of lettering is so distinctive that it can be dated specifically to the middle of the 9th century. Experts conclude that Borobudur must have been built by the Sailendra kings who ruled in Central Java at that time.
Further efforts at restoration by Europeans throughout the next century are well meaning, but ultimately do more damage than good. The sediment and plant life that had shrouded Borobudur for so long had also protected it from the elements. As the galleries are cleared, the porous volcanic stone is exposed to Java's relentless heat and torrential downpours. Throughout most of the 19th century, Borobudur suffers more damage than in the thousand years before.
In 1968, the Indonesian government and the United Nations, working through UNESCO, launch the "Save Borobudur" campaign. Over the next fifteen years, twenty million dollars are raised to support a bold plan: the complete dismantling and reconstruction of the lower terraces of the monument – stone by stone. Professionals from twenty-seven countries join their Indonesian counterparts to carry out the project.
Over one million stones are moved during the course of restoration,
idental discovery rekindles interest in preserving this ancient treasure. J. W. Ijzerman, a Dutch architect involved in a restoration project, walks along the high processional path that surrounds the base of Borobudur. "And he noticed that the moldings of the wall continued underneath a crack that he saw in the floor," says Fontein. "This meant that all these stones must have been added at a time when part of the building was already finished."Ijzerman excitedly calls for a section of the path to be removed. When sixteen layers of stone have been pulled away, Ijzerman discovers another tier of panels quite unlike those of the upper galleries. These are portrayals of hellish tortures mixed with scenes of sweet pleasure. In all, one hundred sixty panels are uncovered. A few scenes had been left unfinished, with instructions to the stone carver inscribed in Sanskrit, and the style of lettering is so distinctive that it can be dated specifically to the middle of the 9th century. Experts conclude that Borobudur must have been built by the Sailendra kings who ruled in Central Java at that time.
Further efforts at restoration by Europeans throughout the next century are well meaning, but ultimately do more damage than good. The sediment and plant life that had shrouded Borobudur for so long had also protected it from the elements. As the galleries are cleared, the porous volcanic stone is exposed to Java's relentless heat and torrential downpours. Throughout most of the 19th century, Borobudur suffers more damage than in the thousand years before.
In 1968, the Indonesian government and the United Nations, working through UNESCO, launch the "Save Borobudur" campaign. Over the next fifteen years, twenty million dollars are raised to support a bold plan: the complete dismantling and reconstruction of the lower terraces of the monument – stone by stone. Professionals from twenty-seven countries join their Indonesian counterparts to carry out the project.
Over one million stones are moved during the course of restoration, 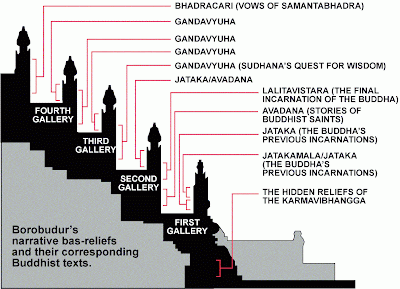 and set aside like pieces of a massive jig-saw puzzle. Thirteen hundred carved panels are taken apart and individually cleaned, catalogued and treated for preservation. And Borobudur becomes a testing ground for new conservation techniques – new procedures to battle the microorganisms eating away at the stone. Experts in engineering, chemistry, biology and archaeology all share their skills to solve the multitude of problems. The restoration takes eight years of labor and unprecedented international cooperation to complete.
and set aside like pieces of a massive jig-saw puzzle. Thirteen hundred carved panels are taken apart and individually cleaned, catalogued and treated for preservation. And Borobudur becomes a testing ground for new conservation techniques – new procedures to battle the microorganisms eating away at the stone. Experts in engineering, chemistry, biology and archaeology all share their skills to solve the multitude of problems. The restoration takes eight years of labor and unprecedented international cooperation to complete.
 idental discovery rekindles interest in preserving this ancient treasure. J. W. Ijzerman, a Dutch architect involved in a restoration project, walks along the high processional path that surrounds the base of Borobudur. "And he noticed that the moldings of the wall continued underneath a crack that he saw in the floor," says Fontein. "This meant that all these stones must have been added at a time when part of the building was already finished."Ijzerman excitedly calls for a section of the path to be removed. When sixteen layers of stone have been pulled away, Ijzerman discovers another tier of panels quite unlike those of the upper galleries. These are portrayals of hellish tortures mixed with scenes of sweet pleasure. In all, one hundred sixty panels are uncovered. A few scenes had been left unfinished, with instructions to the stone carver inscribed in Sanskrit, and the style of lettering is so distinctive that it can be dated specifically to the middle of the 9th century. Experts conclude that Borobudur must have been built by the Sailendra kings who ruled in Central Java at that time.
Further efforts at restoration by Europeans throughout the next century are well meaning, but ultimately do more damage than good. The sediment and plant life that had shrouded Borobudur for so long had also protected it from the elements. As the galleries are cleared, the porous volcanic stone is exposed to Java's relentless heat and torrential downpours. Throughout most of the 19th century, Borobudur suffers more damage than in the thousand years before.
In 1968, the Indonesian government and the United Nations, working through UNESCO, launch the "Save Borobudur" campaign. Over the next fifteen years, twenty million dollars are raised to support a bold plan: the complete dismantling and reconstruction of the lower terraces of the monument – stone by stone. Professionals from twenty-seven countries join their Indonesian counterparts to carry out the project.
Over one million stones are moved during the course of restoration,
idental discovery rekindles interest in preserving this ancient treasure. J. W. Ijzerman, a Dutch architect involved in a restoration project, walks along the high processional path that surrounds the base of Borobudur. "And he noticed that the moldings of the wall continued underneath a crack that he saw in the floor," says Fontein. "This meant that all these stones must have been added at a time when part of the building was already finished."Ijzerman excitedly calls for a section of the path to be removed. When sixteen layers of stone have been pulled away, Ijzerman discovers another tier of panels quite unlike those of the upper galleries. These are portrayals of hellish tortures mixed with scenes of sweet pleasure. In all, one hundred sixty panels are uncovered. A few scenes had been left unfinished, with instructions to the stone carver inscribed in Sanskrit, and the style of lettering is so distinctive that it can be dated specifically to the middle of the 9th century. Experts conclude that Borobudur must have been built by the Sailendra kings who ruled in Central Java at that time.
Further efforts at restoration by Europeans throughout the next century are well meaning, but ultimately do more damage than good. The sediment and plant life that had shrouded Borobudur for so long had also protected it from the elements. As the galleries are cleared, the porous volcanic stone is exposed to Java's relentless heat and torrential downpours. Throughout most of the 19th century, Borobudur suffers more damage than in the thousand years before.
In 1968, the Indonesian government and the United Nations, working through UNESCO, launch the "Save Borobudur" campaign. Over the next fifteen years, twenty million dollars are raised to support a bold plan: the complete dismantling and reconstruction of the lower terraces of the monument – stone by stone. Professionals from twenty-seven countries join their Indonesian counterparts to carry out the project.
Over one million stones are moved during the course of restoration,  and set aside like pieces of a massive jig-saw puzzle. Thirteen hundred carved panels are taken apart and individually cleaned, catalogued and treated for preservation. And Borobudur becomes a testing ground for new conservation techniques – new procedures to battle the microorganisms eating away at the stone. Experts in engineering, chemistry, biology and archaeology all share their skills to solve the multitude of problems. The restoration takes eight years of labor and unprecedented international cooperation to complete.
and set aside like pieces of a massive jig-saw puzzle. Thirteen hundred carved panels are taken apart and individually cleaned, catalogued and treated for preservation. And Borobudur becomes a testing ground for new conservation techniques – new procedures to battle the microorganisms eating away at the stone. Experts in engineering, chemistry, biology and archaeology all share their skills to solve the multitude of problems. The restoration takes eight years of labor and unprecedented international cooperation to complete.In the words of Professor Soekmono, the Indonesian archaeologist who directed the Borobudur Restoration Project: "Borobudur has resumed its old historical role as a place of learning, dedication and training. We might even conclude that the builders of the monument hoped and planned for such continuity. An excellent training program, either for the pilgrim-devotee or for the field technician, is always based on a wish, a fervent wish, that the trainee will achieve what is projected. For the ardent Buddhist it is the Highest Wisdom that leads to the Ultimate salvation, and for the technician the highest degree of expertise that leads to the appropriate fulfillment of his duty. In both cases, Candi Borobudur is the embodiment of such a deeply felt wish. It is a prayer in stone." (Original Sources : PBS Website, Copyright © Public Broadcasting Service
(PBS). All rights reserved., Photo Source : Sabudi Prasetyo)


